Introduction
Enterprise and Data Centers that require the fastest and most dense storage opt for NVMe SSDs for their high-speed PCIe interface. Hard drives are slower and SATA is not that much faster. As new PCIe protocols advance, the adoption for NVMe storage continues to rise.
NVMe SSDs predominantly come in 2 form factors: M.2 and 2.5-inch drives:
- M.2 NVMe SSDs were developed for thin and light laptops, and take a shape similar to a gum stick. These SSDs utilize 4x PCIe lanes and have been well-adopted in desktop and enterprise data center settings. However, data centers require the flexibility of hot-swappable drives that can be serviced without powering down. Therefore, M.2 SSDs in data centers don’t have mainstream appeal for large data storage and are often only used for the boot OS. There are carrier cards that can support hot-swap nature but the M.2 form factor was never built for this purpose.
- 2.5” Drive is the standard width of a normal SATA SSD and small form factor HDD. To adhere to this common sizing, U.2 NVMe SSDs are used in the data center for fast data storage. U.2 NVMe utilizes an identical port to SATA but uses some extra pins on the interface to connect to PCIe lanes directly. U.2 drives are hot-swappable which make it the choice for enterprise NVMe storage but the similar-to-SATA interface limits power and peak performance.
Enterprise and Data Center SSD Form Factor (EDSFF) SSDs have emerged as an important advancement to meet the demand, designed to optimize performance, power efficiency, cooling, and more importantly density. EDSFF SSDs aim to supplement traditional 2.5-inch and M.2 drives by offering purpose-built solutions for enterprise environments that want the efficiency and scalability of NVMe storage while also incorporating appropriate hot-swapping technology. Its higher power draw, larger form factor, and purpose-built nature enable EDSFF to house more storage chips and be more performant with the increased power draw.
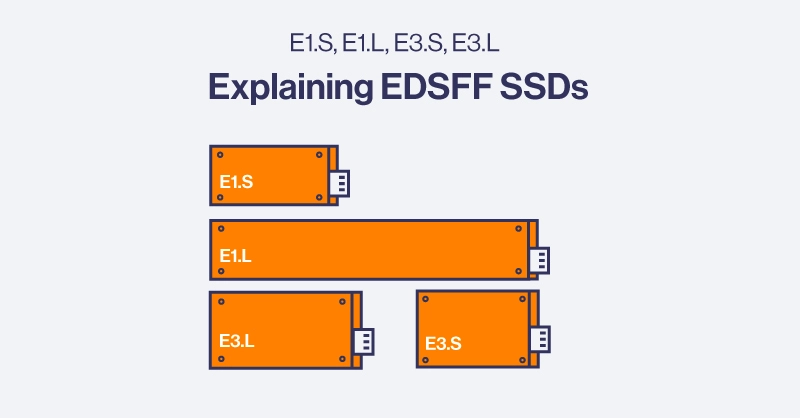
This blog will walk through the different EDSFF form factors—E1.S, E3.S, as well as their longer E1.L and E3.L variants, and explore their impact on modern data centers.
What is EDSFF?
EDSFF, short for Enterprise and Data Center SSD Form Factor, is a standard set by industry leaders to address the limitations of traditional SSD form factors. It's designed with the specific needs of data centers in mind, optimizing for airflow, density, serviceability, and performance. By providing more efficient use of space and power, EDSFF SSDs enable high-density deployments and facilitate seamless scaling for data centers.
Key EDSFF Form Factors
1. E1.S
E1.S is the smallest of the EDSFF SSDs, designed to replace the M.2 form factor in the data center but make it hot-swappable. These E1.S drives are front-mounted and have the width of a 1U chassis. It is optimized for high-density, low-power applications where storage is tightly packed. There are various thicknesses for a heatsink (or lack thereof), in turn drawing more power and having faster performance.
- Use Cases: Ideal for environments that prioritize density overcapacity, such as scale-out cloud storage. E1.S are most often used in 1U storage servers.
- Impact on Data Centers: With its slim design, E1.S enables a higher number of drives per server. This density is beneficial in applications where cost-effective scaling is essential.
2. E1.L
E1.L offers a longer, higher-capacity alternative to E1.S. It can accommodate more NAND flash, making it a better fit for high-capacity use cases. For storage dedicated 1U servers, having E1.L can drastically increase the density of high-speed NVMe storage.
- Use Cases: This form factor suits workloads that need high-density fast storage capacity, such as large databases or AI/ML datasets.
- Impact on Data Centers: E1.L provides high storage density in a compact footprint, making it advantageous for data centers with space constraints but high capacity needs.
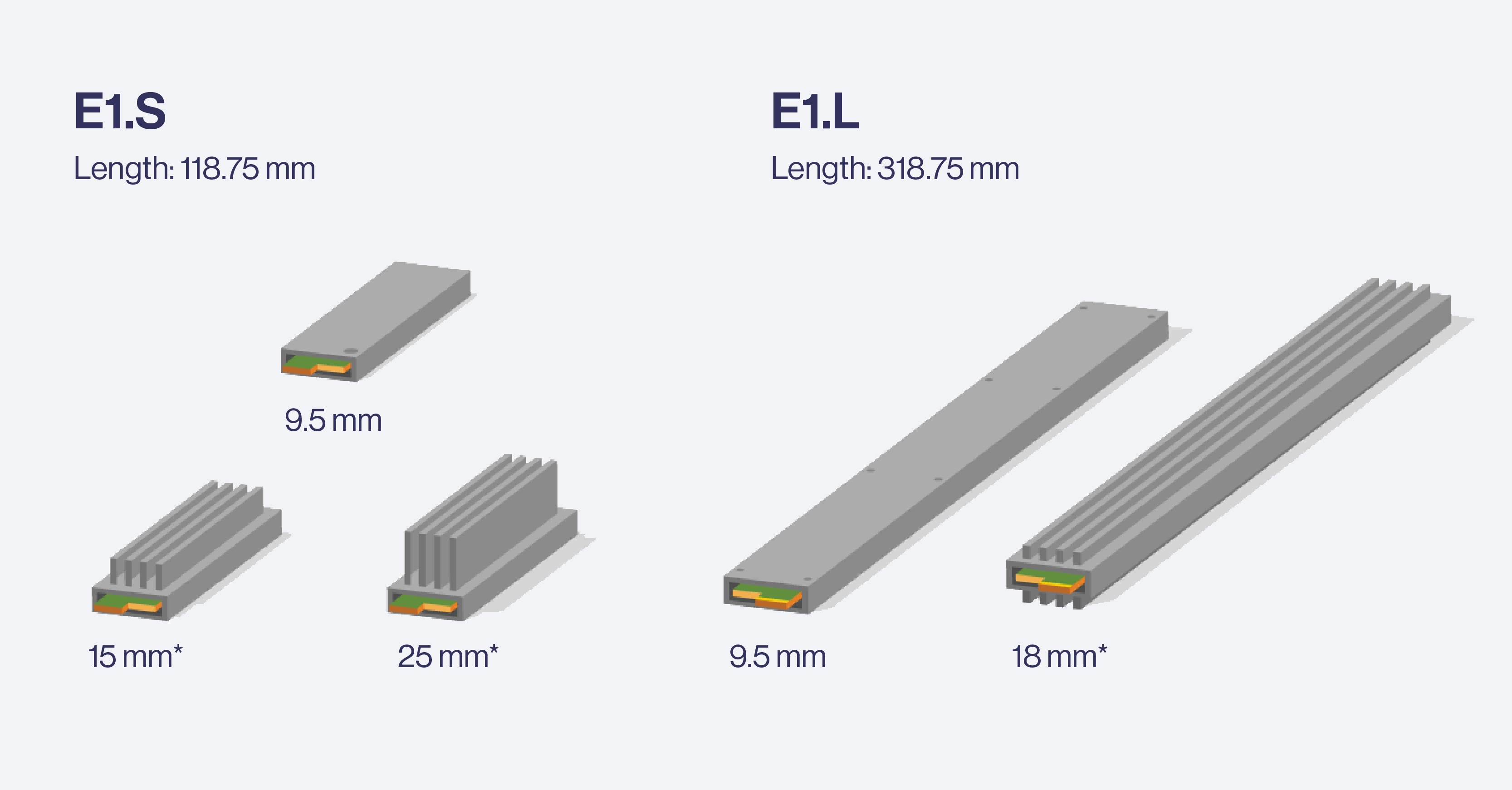
Form Factor | Thickness | Width | Length | TDP |
E1.S 9.5mm | 9.5mm | 33.75mm | 118.75mm | 20 |
E1.S 15mm | 15mm | 33.75mm | 118.75mm | 25 |
E1.S 25mm | 25mm | 33.75mm | 118.75mm | 25 |
E1.L 9.5mm | 9.5mm | 38.4mm | 318.75mm | 25 |
E1.L 18mm | 18mm | 38.4mm | 318.75mm | 40 |
3. E3.S
E3.S is a powerful alternative to the traditional 2.5-inch drive, designed to handle high-performance tasks while providing better airflow and cooling. It has a similar form factor to that of a 2.5" SATA or U.2 drive but uses the EDSFF interface and supports higher power draw and performance. The 2.5" form factor fits the height of a 2U server chassis.
- Use Cases: High-performance computing (HPC), AI, and other data-intensive workloads that benefit from sustained, high-throughput storage.
- Impact on Data Centers: E3.S SSDs deliver improved power and thermal efficiency, allowing data centers to run high-performance applications without compromising on density or cooling requirements.
4. E3.L
The E3.L form factor combines the performance and thermal benefits of E3.S with a larger capacity. The E3.L is slightly longer than E3.S, allowing it to house even more flash storage chips, making it ideal for high-capacity storage solutions. They also allow increased power draw for better performance.
- Use Cases: Perfect for larger, higher-capacity storage arrays where both performance and capacity are necessary.
- Impact on Data Centers: E3.L is highly beneficial in data centers where capacity and performance are paramount. With the larger form factor, data centers can consolidate storage and achieve high capacity without the need for additional physical space.

Form Factor | Thickness | Width | Length | TDP |
E3.S | 7.5mm | 76mm | 112.75mm | 25W |
E3.S 2T | 16.8mm | 76mm | 112.75mm | 40W |
E3.L | 7.5mm | 76mm | 142.2mm | 40W |
E3.L 2T | 16.8mm | 76mm | 142.2mm | 70W |
Benefits of EDSFF SSDs in Data Centers
EDSFF drives bring several notable advantages to data centers, which contribute to their growing popularity:
- Increased Density: EDSFF's compact designs, especially E1.S and E1.L, allow for higher storage densities, enabling data centers to pack more storage into the same or smaller footprint.
- Enhanced Thermal Management: The form factors are engineered for optimal airflow and thermal efficiency, addressing one of the most pressing issues in data center operations. It also supports more efficient use of power relative to legacy form factors.
- Better Serviceability: EDSFF SSDs are hot-swappable, meaning that drives can be replaced without shutting down systems, which minimizes maintenance-related downtime.
With their modular designs and form factors, higher power draw, and data center-specific design, EDSFF SSDs can more easily adapt to future data center advancements and scalability needs. As PCIe generations advance and increase in power or efficiency, EDSFF is easily adaptable. EDSFF is already PCIe Gen 6 ready and we imagine the continued adoption of these types of storage devices for HPC and data-intensive workloads.
Solidigm, a leader in the high-density enterprise storage space, did a study on the adoption rate of EDSFF-type storage in data centers and saw consistent growth and shift towards this new technology over traditional U.2 and M.2 form factors. While U.2 and M.2 will never be outright replaced due to their prevalence in the consumer industry. However, the need for higher-density storage, especially in E1.L and E1.S, is projected to have an even higher adoption rate.
.png)
EDSFF and the Future of Data Center Storage
EDSFF SSDs represent a significant step forward in addressing the unique challenges of data center storage. With their optimized sizes, better cooling, and increased density, EDSFF drives allow data centers to scale efficiently, handle higher workloads, and prepare for future demands. Generative AI, data-intensive HPC like weather modeling and molecular dynamics, and LLMs require massive amounts of computing and fast data to go along with.
As more data centers adopt EDSFF standards, we’ll likely see continued evolution and new standards tailored to emerging data center requirements. For now, E1.S, E1.L, E3.S, and E3.L are setting the stage for a new generation of storage infrastructure that will shape the future of enterprise storage for years to come.
Get a quote on an EDSFF-enabled 1U dense storage server featuring 24x E1.S hot-swap drive bays.

If you have any questions about high-performance storage or are looking for bulk NVMe or SATA storage, contact us for a quote! Or you can explore our Storage Solutions and configure it yourself!