What is SATA and SAS?
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) and SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) are two different types of computer interfaces used for connecting storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs), to a computer system. The Storage is your HDD or SSD that contains all the memory and data stored for your workstation.
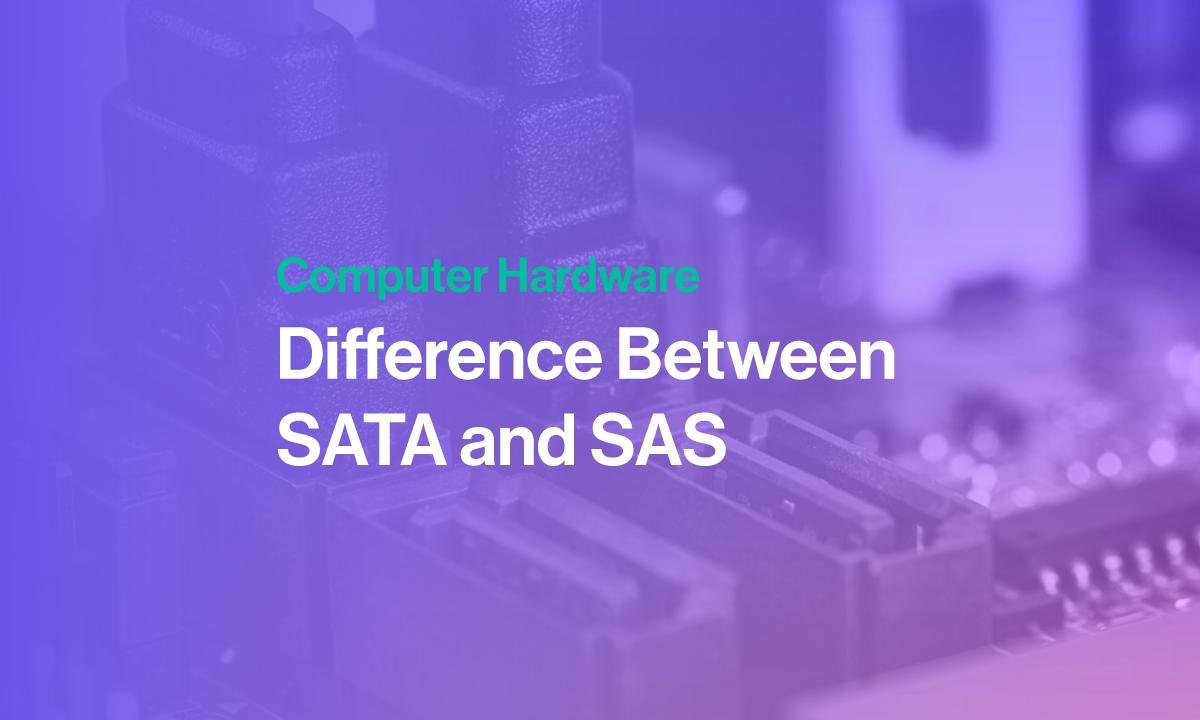
Although they both share the same infrastructure and similar features, only SATA drives can be plugged into a SAS connector whereas a SAS drive cannot be plugged into a SATA connector due to the difference in keying.
So why is there a difference between the two? There are a few main differences between SATA connectors and SAS connectors. Let’s start with the more general overarching differences: Performance, scalability, and reliability.
The Difference Between SATA and SAS
- Performance and Speed: SAS drives generally offer higher performance and faster data transfer rates compared to SATA drives. This makes SAS more suitable for high-demand applications and environments that require quick access to data. SAS drives have lower latency and lower access times enabling faster data transfer rates making it the preferred choice for databases, virtualization, and data-intensive applications that require speed while still being cost-effective compared to other storage devices.
- Compatibility: SAS interfaces are backward compatible with SATA drives, meaning that SATA drives can be connected to SAS ports. However, the reverse is not true. SATA interfaces can only support SATA drives and are not compatible with SAS drives.
- Flexibility and Scalability: SAS interfaces allow for greater flexibility and scalability, making them ideal for complex storage setups. SAS drives can be daisy-chained, enabling the connection of multiple drives to a single controller. This feature simplifies storage expansion and management by
- Cost: SATA drives are generally more cost-effective compared to SAS drives. The affordability of SATA makes it a popular choice for personal computers and consumer-grade devices, whereas SAS drives are more commonly used in enterprise-level environments that require enhanced performance and reliability.
- Use Cases: SATA drives are suitable for everyday computing tasks, including web browsing, multimedia playback, and general file storage. On the other hand, SAS drives excel in scenarios that demand high-speed data access, such as server applications, data centers, and enterprise storage systems.
SATA: An Overview
SATA, or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, is a popular interface used in consumer-grade devices such as desktop computers, laptops, and external hard drives. They are also used in enterprise settings in cold storage where data is not accessed often. It offers a straightforward and cost-effective solution for connecting storage devices. SATA interfaces typically come in three variations: SATA 1.0, SATA 2.0, and SATA 3.0 (also known as SATA III). SATA data transfer rates are up to 6 Gbps.
SAS: An Overview
SAS, or Serial Attached SCSI, is a high-performance interface designed for enterprise-level storage systems. It combines the benefits of SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) and SATA, offering improved speed, reliability, and scalability. SAS interfaces support both SAS and SATA drives, making them versatile options for various storage setups. SAS data transfer rates range from 3 Gbps to 12 Gbps.
How Do I Purchase SATA and SAS?
Many computers come with SATA or SAS connectors included during a purchase, but if you’re building a machine from scratch or optimizing a server, you’ll need to order more connectors separately.
SSD is going to be our recommendation for faster reading and writing of information. The main consideration is how much storage you are looking for because an SSD will have less storage at a similar price point to an HDD which will have more storage at the same price point. If performance is the goal, then SSD is the way to go.
To make it easier for you, you can check out our store page for SAS hard drives, and SATA hard drives. Then, you can take advantage of these filters and look for a specific SSD or HDD based on your preferences.
In short, SAS is generally more expensive than SATA but is usually a better option for servers and process-heavy applications. Most motherboard platforms even at the HEDT workstation level won’t support SAS since it is a specialized storage protocol for a specific workload.
SATA is generally less expensive than SAS, and typically a better choice for desktop and home computer workstations.
However, both of these descriptions are an oversimplification of what each offer and how they function. To grasp a better understanding of the difference between SATA and SAS we have to dive a little deeper.
Other Frequently Asked Questions About SATA & SAS
How many pins does a SATA connector have?
A SATA data cable has 7 pins and a SATA power cable has 15 pins.
How many pins does a SAS connector have?
SAS connectors are usually 7-pin connection points.
What is the purpose of a SATA power connector on the motherboard?
The purpose of the SATA power connector and SATA data connector is to power the device and enable data transmission for a device connected to the bus interface such as hard drives or disk drives.
Get More Helpful Insights in Other Articles
Would you rather go with SATA connectors or SAS connectors after reading about the differences between SATA and SAS? We want to help you make the best decision possible, so please reach out to us! If you have any questions or want to suggest some other topics for us to focus on, please feel free to contact us.
You can find other articles and comparisons elsewhere on the SabrePC blog. Keep a lookout for more helpful articles that will be on the way soon.