DDR5 is the next generation of memory superseding DDR4, and it has been a year since it’s release. We go over what changed between DDR4 and DDR5 as well as go over the newest platforms supporting DDR5.
What is RAM
RAM (Random Access Memory) is a key component in a system responsible for the short-term memory bank that the system can draw quickly. Not enough RAM can result in a sluggish and unresponsive system, and nobody wants that. More RAM is always beneficial but too much can result in diminishing returns. It is always better to run 2 RAM modules in dual-channel versus a single stick of RAM of the same capacity. We've listed the general amounts of RAM needed for running different applications.
- 8GBs: Browsing Internet, Emails, Streaming Movies
- 16GBs: Spreadsheets, Light Gaming, Multitasking Programs
- 32GBs: HD Gaming, Content Creation, Basic Video Editing, Graphic Design
- 64GBs: 3D Modeling, 4K/8K Video Editing, Simulation, Game Dev.
- 128GB and More: Deep Learning, Database Server, HPC applications
What is the difference between DDR4 and DDR5?
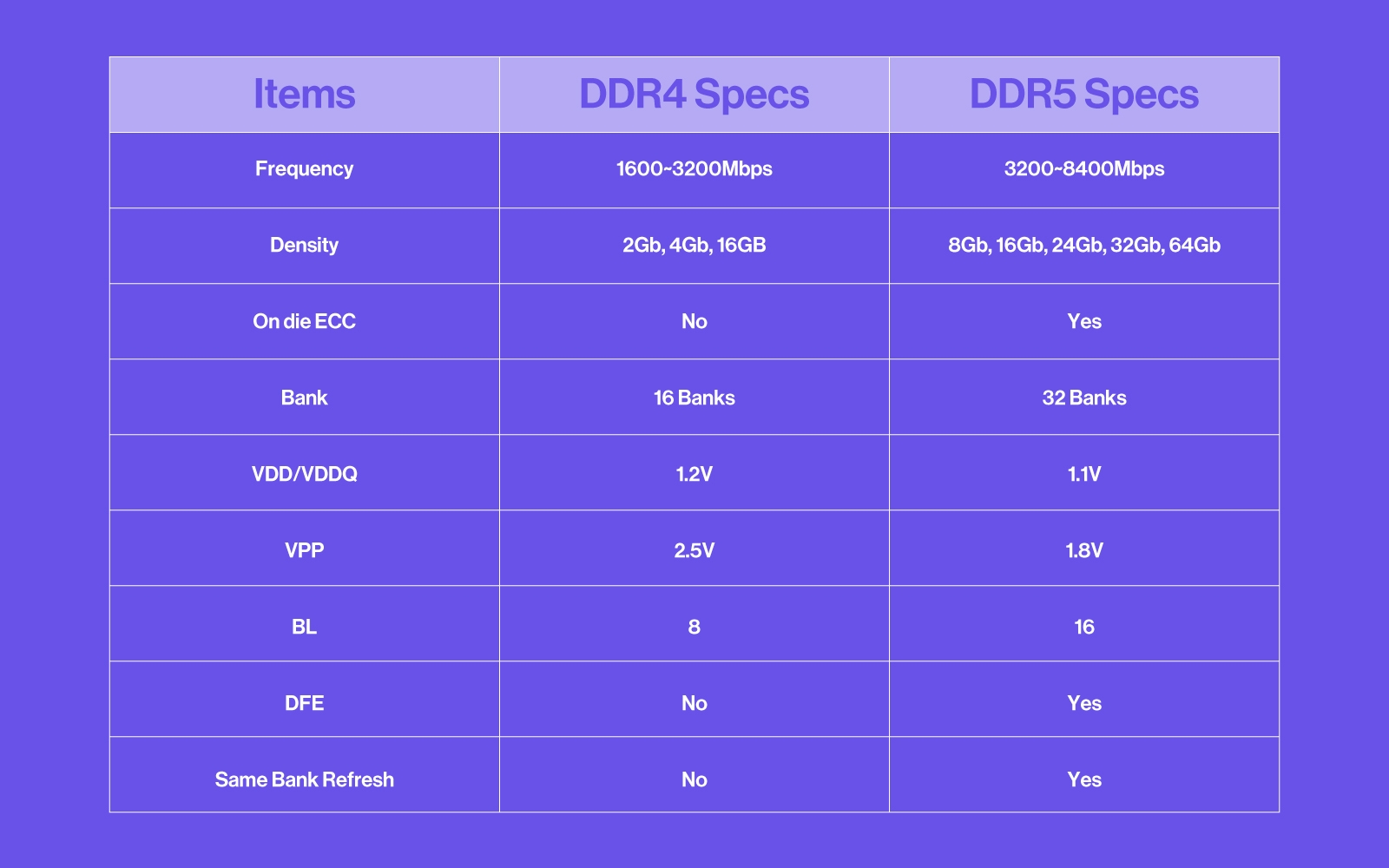
DDR4, first introduced 10 years ago, has undergone many changes in DDR5 such as to pins location, bit transfer, max speed, and architecture A new generation of memory addresses the higher computational demands and complexity of newer CPUs, GPUs, storage, and protocols. DDR5 has been out for about a year and has only recently landed in consumers' hands. Since next-generation Intel Alder Lake and AMD Zen 4 (both supporting DDR5) release later this year, we want to provide as much information about DDR5 and its differences from the last generation.
DDR5 vs DDR4 Pins and Installation
DDR5 is the same length and contains the same number of pins as DDR4 models (288 pins). However, DDR5 cannot be used interchangeably with DDR4 since the keying notch is in slightly different locations. Due to the rework of the pins, each pin on the module sticks holds different functions. To accompany the new DDR5 memory, you will need to purchase a new DDR5 motherboard, as well as a CPU that supports DDR5 memory.
DDR5 Dual Bit Subchannel
DDR5 changes how data transfers through the bit-bus. DDR4 sports single 64-bit channel whereas DDR5 utilizes dual 32-bit channels equating to 64 bits transferred at one time. This allows more precise data transfers instead of waiting for an entire 64-bit transfer over the bit-bus. Also, DDR5 32 banks doubling the 16 banks in DDR4 to effectively match the total bit size.
When installing 2 RAM modules for dual-channel configurations, DDR5 will use a deliver 4 x 32-bit configuration in rapid succession as opposed to the traditional 2x 64-bit configuration on DDR4. DDR5’s data transfers are more efficient resulting in lower power draw.
DDR5 Max Capacity
DDR5 will offer larger sizes per stick of RAM for enteprise: up to 32GB per module for consumers, and up to 256GB for enterprise! Currently, DDR4 also supports up to 32GBs per module for consumer but, commonly has 128GB for enterprise. It is still common for DDR5 to use 128GB modules in enterprise settings.
While higher capacity RAM per module will not change for the consumer market, the double the capacity in server RAM will increase the capacity of memory drastically per server.
DDR5 vs DDR4 Speeds
Not only has the density increased but also the speed. DDR4 peak speeds are 3200 mega transfers per second (usually denoted after RAM capacity). DDR5 starts at 4800 and can reach upwards of 6400 mega transfers per second and more as DDR5 develops. These higher data rates mean an increase in memory bandwidth for higher speeds. Keep in mind, that a double in data rates does not equate to double the performance.
DDR5 PMIC (Power Management Integrated Circuit)
The larger capacity DDR5 will need to distribute power more efficiently. In previous DDR generations, the motherboard directly provided voltage to RAM slots limiting motherboards to certain RAM speeds and voltages. DDR5 incorporated a PMIC that takes a single 5V from the motherboard and then distributes it among the RAM dies in a more controlled and efficient way. The addition of a PMIC allows for better voltage regulation and overclocking, as well as reduces wasted wattage and electrical noise. DDR5 lowered the default voltage from 1.2 to 1.1, a small change but has an impact on decreasing power consumption and a healthy advancement for preserving battery life in laptops and handhelds.
DDR5 has Error Correction Code Standard
Error correction code (ECC) memory is a type of RAM mainly found in workstations and servers but not in consumer-level modules. ECC automatically detects and corrects memory errors to prevent data corruption and is valued by professionals and businesses with critical data. Non-ECC RAM suffers a 0.6% failure rate; ECC-equipped RAM has a tiny 0.09% failure rate, almost six times the stability. DRR5 now incorporates ECC as standard in all modules, both in workstations and servers, as well as consumer-grade DDR5.

Should You Get a DDR5 Platform
It has been over a year since DDR5 entered into the consumer and enterprise market for implementation in our systems. Keep in mind that upgrading to DDR5 does not offer insane levels of performance but, DDR5 is the future will soon be the standard and more and more applications will soon benefit from the advantages of DDR5.
If you are looking for an upgrade in just your memory or are on the latest DDR4 generation (12th Gen Intel Core or 3rd Gen AMD Ryzen 5000) we think upgrading solely for DDR5 would not be the best choice since it requires the purchase of a new CPU, motherboard, etc. for marginal gains and would wait another generation.
However, if you plan to purchase or build a new workstation on the DDR5 platform like Intel 13th Gen, Xeon W-3400, AMD Ryzen 7000, and Threadripper 7000 (coming soon), DDR5 is inevitable. A newer system is a great investment for futureproofing while taking advantage of DDR5's new capabilities as the latest and greatest innovations in the PC industry.
SabrePC stocks the DDR5 RAM you need for your next build! Be sure to pair it with a DDR5 compatible motherboard! If you are unsure of what you need, contact SabrePC today!


